Glossary: Fitness Terminology Explained in Layman’s Terms

A
Aerobic Exercise
The word ‘aerobic’ is defined by “with oxygen”. Aerobic exercise is a continuous, rhythmic cardio exercise that increases the breathing, heart rate and the body’s need for oxygen.
Anaerobic Exercise
Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that is made up of short burst and high intensity training without using oxygen. The high intensity exercise uses glucose instead of oxygen for fuelling the body.
B
Balance Training
Exercises or movements used to improve stability and fall prevention. Static and dynamic exercises are commonly applied to strengthen muscles used for keeping the body upright for daily activities.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
BMR is the number of minumum calories required by the body to survive, such as breathing and keeping the heart beating. See Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR).
Beats per Minute (BPM)
BPM is the number of heartbeats in a minute.
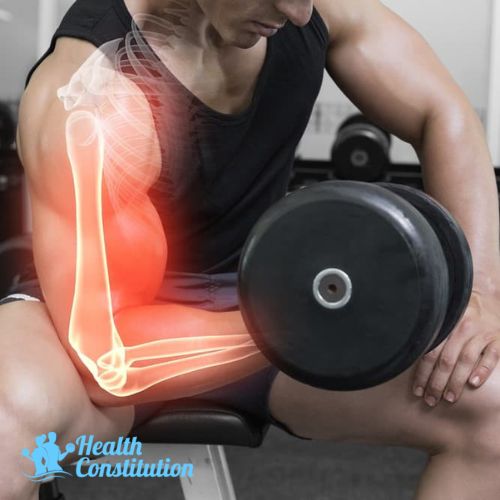
Biceps
The biceps is the large muscle at the front of the upper arm. Biceps are used when carrying heavy items, throwing a ball, doing curls, and boxing.
Body Composition
Body composition is used to refer to the distribution of fat, muscles, bone and water in the body. This is a common terminology used by health professionals as well as within the fitness community.
Body Conditioning
A type of exercise that targets the whole body to improve flexibility, endurance and muscle strength.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI is a formula (kg/m²) used to calculate and classify a person’s weight relative to their height. The weight classification consist of “underweight”, “healthy”, “overweight”, and “obese”.
Bodybuilding
It is an activity that involves enhancing the muscles through hypertrophy via exercise for aesthetic purposes. Bodybuilding focuses on maintaining a symmetrical muscular build for physical appearance instead of strength training like power lifting or functional training.
Bodyweight Exercise
It is a type of exercise that uses the person’s own weight as resistance for strength training. An example of bodyweight exercise is squats.
C
Calisthenics
It is a type of strength training involving movements such as jumping, pushing, bending with levels of intensity and rhythm using mainly the person’s own bodyweight and minimal equipment.
Cardio
Cardio is a type of exercise intended to keep the heart rate up over a period of time. It can promote heart health and burn calories. Read this article for more details on cardio exercise.
Circuit Training
It is a type of body conditioning exercise that involved a series of exercises usually consisting of resistance training, high-intensity activities and endurance training with a short period of rest in between exercises. Circuit training is done with the purpose of improving endurance and strength.
Concentric Contraction
Concentric contraction describes the movement whereby the muscle is shorten. An example of concentric movement/ exercise is bicep curl when the dumbbell moves towards the person doing it. See Eccentric Contraction. Find out more from concentric vs eccentric exercises.
Cool Down
A low-impact physical activity done after a an intense workout with the aim to gradually allow the body to return to a resting state. Check out this article on ways to cool down after exercise. See Warm Up.
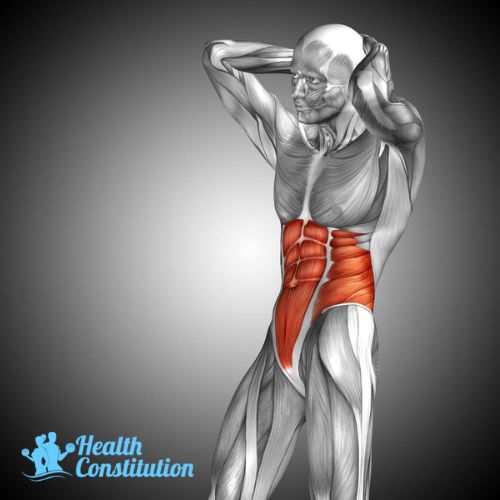
Core
A muscle group containing the abs, obliques, hips and lower back muscles. Core exercises train these muscles to work together for postural and spine health as well as stability for everyday activities.
Cross Training
Cross training is a way to vary a regular fitness routine by incorporating different types of exercises other than the regular exercise. It is a good practice to strengthen other muscle groups not often used in regular routine to minimise the risk of injury.
D
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)
Muscle ache that occur after 1-2 days of workout. Doing strenuous exercises or starting a new workout can result in delayed onset muscle soreness. Learn more about DOMS from a physiotherapist in this article.
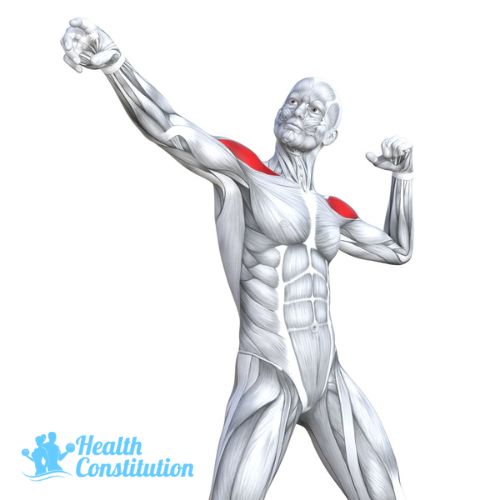

Delts (Deltoids)
Deltoid muscles are located in the shoulder and its primary function is to allow the arms to roate in different directions.
Dynamic Stretching
Dynamic stretching is a type of functional stretching that incorporates movements of the exercise that is about to be performed. An example of dynamic stretching is high knees. See Static Stretching.
E
Eccentric Contraction
Eccentric contraction is the lengthening of muscle during a movement. An example is the movement of bicep curl having the dumbbell away from the person doing it. See Concentric Contraction. Find out more from concentric vs eccentric exercises.
F
Flexibility
It refers to the ability of joints to move in a range of motion freely without pain. Stretching and certain exercises can help improve flexibility.
Free Weight
Heavy objects like dumbbells and barbells for the purpose of training that are not attached to any other equipment.
Functional Training
A type of training that helps prepare your body to do daily activities like lifting, squatting, pushing, pulling, bending and twisting. Muscles are trained to make the performance of everyday activities easier, safer and more efficient.
G
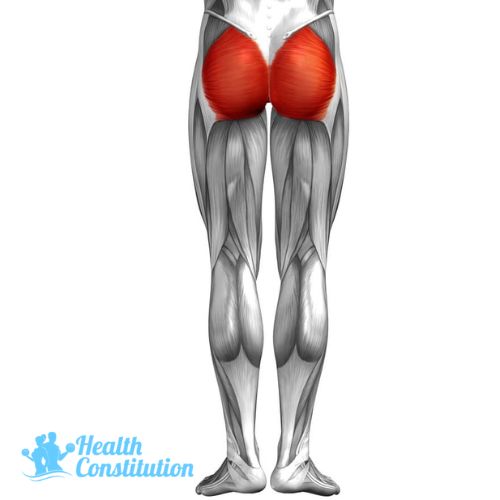
Glutes (Gluteus Maximus)
Muscle of the buttocks, which is important for lower back support.
H
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT is a type of training that incorporates short sessions of highly-intensed workouts with brief recovery period. This training maximise the usefulness of anaerobic activity. For more detailed explanations and examples, visit this article on HIIT.
Hypertrophy
Increase of muscle size from exercise efforts, commonly achieved from lifting weights.
I
Isokinetic Exercise
Isokinetic exercise is a strength training exercise that is achieved via exercise machines that has variable resistance while the rate of movement is constant. Read this article for more info on isometric vs isotonic vs isokinetic exercise.
Isometric Exercise
An exercise where the muscles contract and in a single position. An example of isometric exercise is holding a plank.
Isotonic Exercise
A movement where the muscles are kept at a constant tension. An example of isotonic exercise is squats.
L
Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is the product of the glucose being broken down by the body produce energy to sustain the exercise in the absence of oxygen. It is usually produced during intense exercise sessions.
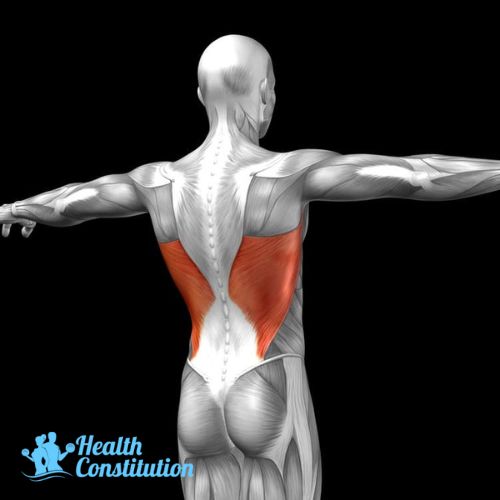
Lats (Latissimus Dorsi)
A large muscle located in the middle and lower back area, connecting the spine and arms. Its main functions are adduct, extend and internally rotate shoulder. The lats can also help support good posture.
Lean Mass
The total body weight excluding fat mass.
Low-Intensity Interval Training (LISS)
It is a steady state type of cardiovascular exercise. Aerobic exercise is an example. Check this article to learn more about LISS.
M
Moderate Intensity
Physical activity that increases the heart rate within 50% to 70% of the maximum heart rate. The maximum heart rate depends on the person’s age.
P
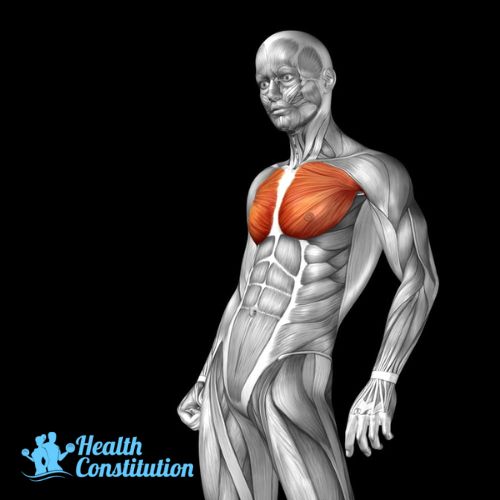
Pecs (Pectoralis Major)
The muscle in the upper chest area. Pushups is an example that utilises the pecs.
Plyometrics
Pyometrics is a type of jump training exercises that aims to work on building muscle power by having the muscle exert maximum force in a brief period. Burpees and box jumps are common exercises used in plyometrics training.
Q
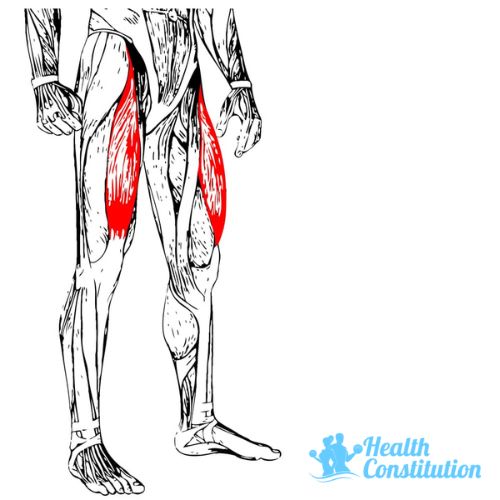
Quads (Quadriceps)
The muscle located at the front of the thigh.
R
Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
It is a numbered scale (from 1 to 10) used to measure the perceived exertion or intensity during exercise.
Recovery
The time it takes to rest after exercise before the start of another set.
Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
The number of calories the body burns while at rest. See Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR).
S
Static Stretching
A type of stretching that focuses on a single muscle group at a time. Holding a stretch for a short period of time (about 30 to 45 seconds) while standing or sitting down is classified as static stretching. See Dynamic Stretching.
Strength Training
A type of training that aims to improve strength and endurance. Strength training is also known as resistance training, where resistance is used to make the muscles contract and build strength.
T
Tabata
Tabata is a high-intensity training that can be done is 4 minutes, with intervals of 20 seconds intense exercise followed by 10 seconds of rest.
Toning
To reduce fat so muscles can appear more defined, not with the intention to increase muscle mass.
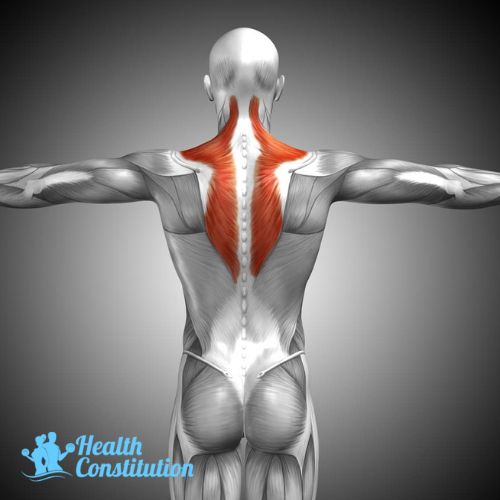
Traps (Trapezius)
Large muscles located at the upper back. Its primary function is to support the arms and shoulders, allowing the scapula to move.
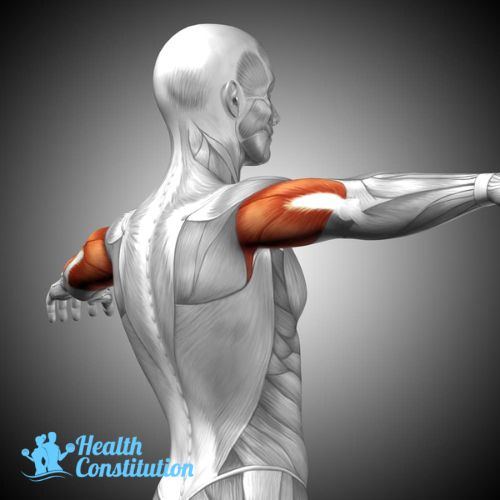
Triceps
The muscle at the back of the upper arm. Triceps are used when doing pushups or pullups.
W
Warm Up
A physical activity done to gradually increase the body temperature to prepare for the exercise that is about to be done and to minimise the risk of injury. See Cool Down.
Weight Training
A type of strength training that utilises free weights like dumbbell and barbell or weight machines to develop muscle strength.